New Facing Targets Sputtering System
Overview | Features | Principle | Applications | Product Information
NFTS Applications
NFTS Technology Fields | Low Temperature Crystallization | Mass Production | Performance | TEM Images | Publications
Crystallization of an oxide thin film at low temperature
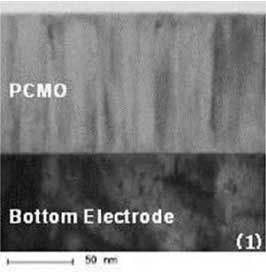
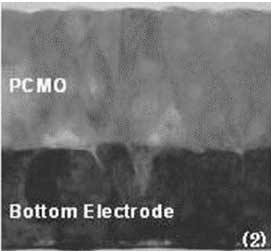
TEM Images of Specimen PCMO films
Demand for oxide or nitride thin films with high quality crystal structure have increased in some applications. The chemical vapor deposition (CVD) methods are widely used to produce these film films. The methods can produce these films because they utilize chemical reaction of processed gases to produce thin films. However, CVD are high cost and unecological processes, since CVD equipment requires some apparatuses to safely dispose of the dangerous processed gases.
The magnetron sputtering (MS) methods are cost effective and safe processes compared to CVD, because MS methods do not utilize dangerous processed gasses to produce thin films. However, MS methods are difficult to produce oxide or nitride thin films with high quality crystal structure. This is because thin films depositing on substrate surfaces are bombarded by particles with high kinetic energy such as negative ions, electrons and Ar atoms. In some cases, the bombardments of these particles may supply some energy to the thin films depositing on substrate surface and may promote crystallization of the thin films. But, in many cases, the bombardments can bring about degradation of the thin films such as strong internal stress, defects in grain boundary and weak bonds among atoms composing the thin films. Therefore, in order to produce oxide or nitride thin films with high quality crystal structure by MS, high substrate temperature is required to recover the degradation of the films.
NFTS technology can prepare oxide or nitride thin films with high quality crystal structure at low temperature compared to the MS methods. NFTS plasma sources confine sputtering plasma in the space between facing targets, and the substrate is positioned outside the facing targets. Therefore, the thin films depositing on the substrate surfaces are rarely bombarded by the particles with high kinetic energy. Figure 10 shows each cross sectional view of oxide thin film PCMO (Pr0.7Ca0.3MnO3) prepared by NFTS and MS methods on 6 inch Si wafer observed under Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)